Since the advent of lasers, people have begun to study how to use lasers as tools to process materials. As early as the 1970s, the automotive industry began experimenting with laser processing. The first industrial application of laser welding for plastics was in 1998 when Marquardt used semiconductor lasers to mass-produce electronic car keys. The key cover of black polymer (PA) material was soldered to the same black but transparent to the laser wavelength. PA key shell.
According to the molecular structure plastics can be divided into three types: thermoplastic materials, thermosetting materials and synthetic rubber. At present, there are many researches and applications on laser welding of thermoplastic materials. Below we will briefly describe the laser welding technology and research progress for thermoplastic materials from three aspects.
I. Process and method of laser welding
The laser welding of thermoplastic materials is mainly by laser transmission welding. This method has certain requirements on the properties of the two materials to be welded, that is, the above thermoplastic layer is transparent to the laser wavelength used, and the lower thermoplastic layer can absorb the laser energy. The laser beam passes through the transparent upper layer material to the lower layer material, and the surface of the lower layer material is melted by absorbing laser energy. At this time, the two materials are welded together by molecular coupling under a certain pressure. Since the laser is non-mechanically contacted to focus on the surface of the underlying material, the thermal effects caused by the laser are localized, so this method avoids mechanical and thermal damage to the material being welded. At present, about 20% of the total processing of thermoplastic materials is based on laser welding.
According to different welding tasks and the requirements of laser welding, there are roughly the following processes.
Contour welding is the simplest and most widely used welding process. At the time of welding, the laser beam moves through the optical system and the galvanometer on the object to be welded or the laser beam is stationary to be moved by the welded object. The interaction time between the laser and the object being welded depends on the beam focus size and moving speed, which affects the soldering time and effect. Contour welding is a very flexible welding process that enables complex three-dimensional welding and is used in a wide range of applications in the packaging industry.
Mask soldering is a process based on a profile soldering or a synchronous soldering method by means of a mask, the principle of which is similar to that of lithography on chip fabrication. This process is primarily used on complex geometric weld patterns with a minimum seam width greater than 100 μm. The mask is often made of sheet or metallized glass. Since the mask is cumbersome to make, the mask is only for one soldering geometry pattern, so mask soldering often lacks flexibility, but is suitable for high-volume soldering.
Quasi-synchronous welding is a process that combines contour welding and simultaneous welding. The laser beam is moved through the galvanometer at an extremely fast speed of up to 10 m/s over the weld and repeated scans several times, so that the entire weld zone melts at the same time, with the same effect as synchronous welding. By the simultaneous melting process, the quasi-synchronous welding and the simultaneous welding method are equally suitable for the bridge welding of two adjacent components having large gaps.
In synchronous welding, the laser beam simultaneously illuminates the weld zone, thereby significantly reducing weld processing time and allowing bridge welding of two adjacent components having large gaps. Compared to contour welding, the portion welded by the simultaneous welding method is more robust due to the longer laser action time.
2. The color of the welded plastic
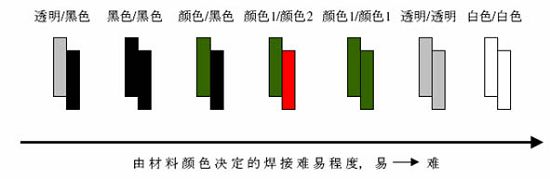
One of the research topics in laser plastic welding is the color matching of the two welded parts, which is determined by the principle of laser transmission welding used. The figure below shows the ease of soldering due to the difference in material color. The first successful implementation of the transparent color – laser welding of black materials. In addition to this, the welding of black-black materials has also been widely used.
Since the Benzo absorption band of the polymer-constituting polymer is usually located in the ultraviolet and far-infrared regions, only CO2 lasers were originally used for laser welding research. However, the optical absorption characteristics of plastics can be greatly changed by doping and adding pigments, so that the absorption of plastics in the visible and near-infrared regions is greatly enhanced, and the original laser-transparent material becomes a laser absorbing material, so that the conventional Nd:YAG solid-state laser Both (1064 nm and doubling 532 nm) and high power GaAs semiconductor lasers (800 nm to 1000 nm) and new fiber lasers can be used as light sources for laser welding. Pigmentation also changes the characteristics and parameters of the original plastic soldering, making it more suitable for a particular application.
3. Matching of welded materials
It is the matching of welding materials that is studied almost simultaneously with the material color. Most of the materials currently used in the industry for laser welding are thermoplastic materials (Thermoplastic, TP), which constitute TP-TP welding. Since the laser transmission welding used is non-contact, these thermoplastic materials can also be welded to other materials, such as Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE). Thermoplastic synthetic rubber because of the elasticity and flexibility of thermoplastic and synthetic rubbers with thermoplastic materials, and its welding processing temperature and cooling time are very similar to thermoplastic materials, so laser transmission welding can be easily used. Achieve TP-TPE welding. Due to the feel and friction of TPE, the first application of TP-TPE welding in the automotive industry is the manufacture of automotive steering wheels. In addition, TPE and TPE can also be welded together by laser transmission welding to form a TPE–TPE weld.
A new direction in material collocation research is the laser welding of plastics to metals and ceramics. For example, plastic is indirectly heated by laser light, the contact surface melts, and then surrounds the metal, forming a very strong bond with the metal.
According to the molecular structure plastics can be divided into three types: thermoplastic materials, thermosetting materials and synthetic rubber. At present, there are many researches and applications on laser welding of thermoplastic materials. Below we will briefly describe the laser welding technology and research progress for thermoplastic materials from three aspects.
I. Process and method of laser welding
The laser welding of thermoplastic materials is mainly by laser transmission welding. This method has certain requirements on the properties of the two materials to be welded, that is, the above thermoplastic layer is transparent to the laser wavelength used, and the lower thermoplastic layer can absorb the laser energy. The laser beam passes through the transparent upper layer material to the lower layer material, and the surface of the lower layer material is melted by absorbing laser energy. At this time, the two materials are welded together by molecular coupling under a certain pressure. Since the laser is non-mechanically contacted to focus on the surface of the underlying material, the thermal effects caused by the laser are localized, so this method avoids mechanical and thermal damage to the material being welded. At present, about 20% of the total processing of thermoplastic materials is based on laser welding.
According to different welding tasks and the requirements of laser welding, there are roughly the following processes.

Contour welding is the simplest and most widely used welding process. At the time of welding, the laser beam moves through the optical system and the galvanometer on the object to be welded or the laser beam is stationary to be moved by the welded object. The interaction time between the laser and the object being welded depends on the beam focus size and moving speed, which affects the soldering time and effect. Contour welding is a very flexible welding process that enables complex three-dimensional welding and is used in a wide range of applications in the packaging industry.
Mask soldering is a process based on a profile soldering or a synchronous soldering method by means of a mask, the principle of which is similar to that of lithography on chip fabrication. This process is primarily used on complex geometric weld patterns with a minimum seam width greater than 100 μm. The mask is often made of sheet or metallized glass. Since the mask is cumbersome to make, the mask is only for one soldering geometry pattern, so mask soldering often lacks flexibility, but is suitable for high-volume soldering.
Quasi-synchronous welding is a process that combines contour welding and simultaneous welding. The laser beam is moved through the galvanometer at an extremely fast speed of up to 10 m/s over the weld and repeated scans several times, so that the entire weld zone melts at the same time, with the same effect as synchronous welding. By the simultaneous melting process, the quasi-synchronous welding and the simultaneous welding method are equally suitable for the bridge welding of two adjacent components having large gaps.
In synchronous welding, the laser beam simultaneously illuminates the weld zone, thereby significantly reducing weld processing time and allowing bridge welding of two adjacent components having large gaps. Compared to contour welding, the portion welded by the simultaneous welding method is more robust due to the longer laser action time.
2. The color of the welded plastic
One of the research topics in laser plastic welding is the color matching of the two welded parts, which is determined by the principle of laser transmission welding used. The figure below shows the ease of soldering due to the difference in material color. The first successful implementation of the transparent color – laser welding of black materials. In addition to this, the welding of black-black materials has also been widely used.
Since the Benzo absorption band of the polymer-constituting polymer is usually located in the ultraviolet and far-infrared regions, only CO2 lasers were originally used for laser welding research. However, the optical absorption characteristics of plastics can be greatly changed by doping and adding pigments, so that the absorption of plastics in the visible and near-infrared regions is greatly enhanced, and the original laser-transparent material becomes a laser absorbing material, so that the conventional Nd:YAG solid-state laser Both (1064 nm and doubling 532 nm) and high power GaAs semiconductor lasers (800 nm to 1000 nm) and new fiber lasers can be used as light sources for laser welding. Pigmentation also changes the characteristics and parameters of the original plastic soldering, making it more suitable for a particular application.
3. Matching of welded materials
It is the matching of welding materials that is studied almost simultaneously with the material color. Most of the materials currently used in the industry for laser welding are thermoplastic materials (Thermoplastic, TP), which constitute TP-TP welding. Since the laser transmission welding used is non-contact, these thermoplastic materials can also be welded to other materials, such as Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE). Thermoplastic synthetic rubber because of the elasticity and flexibility of thermoplastic and synthetic rubbers with thermoplastic materials, and its welding processing temperature and cooling time are very similar to thermoplastic materials, so laser transmission welding can be easily used. Achieve TP-TPE welding. Due to the feel and friction of TPE, the first application of TP-TPE welding in the automotive industry is the manufacture of automotive steering wheels. In addition, TPE and TPE can also be welded together by laser transmission welding to form a TPE–TPE weld.
A new direction in material collocation research is the laser welding of plastics to metals and ceramics. For example, plastic is indirectly heated by laser light, the contact surface melts, and then surrounds the metal, forming a very strong bond with the metal.
Thin Brass Padlock low prices, high quality, loved by people around the world.
Suitable suitcase, drawer, door locks and other places does not store valuables.


Material: Brass Lock body, cylinder, chrome plated shackle
Purpose: lock boxes, cabinets, doors, etc.
Features lock all-copper, shackle sturdy rustproof
Thin Type Brass Padlock,Thin Brass Lock,Gate Brass Padlock,Single Skin Brass Padlock
Shengping Safety Protection Locks Manufacturer , http://www.chinajiuzhou.com