In 1989, Nernst discovered the phenomenon of ionic conduction of stabilized zirconia at high temperatures. In the following period, although various studies have been carried out on this kind of ionic conductive substance, solid electrolyte, progress has been made. Smaller. Among all solid electrolytes, zirconia is currently the most widely used research and development application, and it has been widely used in high temperature technology, especially high temperature testing technology.
Compared with the existing oxygen measuring instruments (such as magnetic oxygen analyzer, electrochemical oxygen meter, meteorological chromatograph, etc.), the zirconia oxygen measuring instrument has a simple structure, a short response time (0.1 to 0.2 S), and a wide measuring range ( From ppm to percentage), the use temperature is high (600 ~ 1200 ° C), reliable operation, easy installation, small maintenance and so on.
1 Oxygen measurement principle of zirconia oxygen meter
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the principle of oxygen measurement by a zirconia oxygen meter.
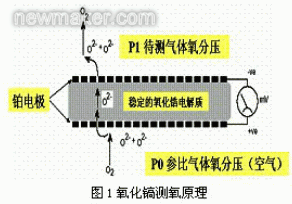
A porous platinum (Pc) electrode is sintered on both sides of the zirconia electrolyte (ZrO tube). At a certain temperature, when the oxygen concentration on both sides of the electrolyte is different, oxygen molecules on the high concentration side (air) are adsorbed on the platinum electrode. The oxygen ion O2- is formed in combination with the electron (4e) to positively charge the electrode. The O2-ion migrates through the oxygen ion vacancies in the electrolyte to the n-electrode on the low oxygen concentration side to emit electrons, which are converted into oxygen molecules, and the electrode is negatively charged. The reaction formulas of the two electrodes are:
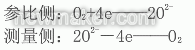
Thus, a certain electromotive force is generated between the two electrodes, and the zirconia electrolyte, the Pt electrode, and the gas having different oxygen concentrations on both sides constitute an oxygen probe, that is, a so-called zirconia concentration battery. The electromotive force E between the two stages can be obtained from the Nernst formula:
Where: E - concentration battery output, mV;
R - ideal gas constant, 8.314 W · S / mol;
T--absolute temperature, K;
n - the number of electron transfer, here is 4;
F--Faraday constant, 96500C;
P0 - the percentage of oxygen concentration in the reference gas;
P1 - the percentage of oxygen concentration of the gas to be tested.
It is the basis of zirconia oxygen measurement. When the temperature of the zirconia tube is heated to 600-1400oC, the gas of high concentration side uses the gas of known oxygen concentration as the reference gas. If air is used, P0=20.6%. This value is combined with the constant term in the formula, and the actual zirconium battery has a temperature difference potential, a contact potential, a reference potential, and a polarization potential, thereby generating a local potential C (mV).
The actual calculation formula is:

It can be seen that if the output electromotive force E of the oxygen probe and the absolute temperature of the gas to be measured can be measured, the oxygen partial pressure (concentration) P of the gas to be measured can be calculated. This is the basic principle of oxygen measurement by zirconia oxygen analyzer.
2 oxygen probe form
According to different detection methods, zirconia oxygen analyzer probes are divided into two categories: sampling and detection oxygen probes and in-line oxygen probes.
1, sampling detection
The sampling detection method is to introduce the gas to be measured into the zirconia detection chamber through the guiding tube, and then heat the zirconia to the working temperature (above 750 ° C) through the heating element. Zirconium oxide is generally tubular and the electrode is a porous platinum electrode (Fig. 2). The advantage is that it is not affected by the temperature of the test gas, and the oxygen content in various temperature gases can be detected by using different draft tubes. This flexibility is used in many industrial online tests. The shortcoming is that the reaction time is slow; the structure is complicated, and the detection precision is easy to be affected; when the detected gas impurities are large, the sampling tube is easily blocked; the porous platinum electrode is easily damaged by corrosion of sulfur, arsenic, etc. in the gas and clogging of fine dust; The heater is generally heated by an electric furnace wire and has a short life.
When the temperature of the gas to be detected is low (0 ° C ~ 650 ° C), or when the gas to be tested is relatively clean, it is suitable for sampling type detection methods, such as nitrogen measurement by a nitrogen generator, and oxygen measurement in a laboratory.
2, inline detection oxygen probe
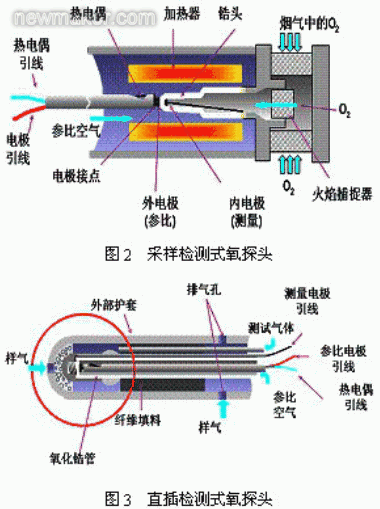
In-line detection is to directly insert zirconia into the high-temperature gas to directly detect the oxygen content in the gas. This detection method is suitable for the temperature of the detected gas at 700 °C ~ 1150 °C (special structure can also be used for high temperature of 1400 °C) ), it uses the high temperature of the gas to be measured to bring the zirconia to the operating temperature without the need for an additional heater (Figure 3). The key to the in-line oxygen probe is the high temperature sealing and electrode problems of ceramic materials.
The following is a list of the construction of two in-line oxygen probes.
(1) Monolithic zirconia tube
This form was developed from the form of a zirconia tube used in the sampling detection method, which is to lengthen the original zirconia tube so that the zirconia can directly extend into the high-temperature gas to be measured. This structure does not require consideration of high temperature sealing problems.
(2) In-line zirconia oxygen analyzer probe
Since the zirconia needs to be directly inserted into the detection gas, the length of the oxygen probe is required to be high, and the effective length is about 500 mm to 1000 mm, and the special environmental length is up to 1500 mm. Moreover, the detection accuracy, working stability and service life have high requirements. Therefore, the in-line oxygen probe is difficult to adopt the integral zirconia tubular structure of the conventional zirconia oxygen probe, and more zirconia and oxidation are required. The structure of the aluminum tube connection. Sealing performance is one of the most critical technologies for this zirconia oxygen probe. At present, the most advanced connection method in the world is to permanently weld zirconia and alumina tubes. The sealing performance is excellent. Compared with the sampling type detection method, the in-line detection has obvious advantages: zirconia is in direct contact with gas. The detection precision is high, the reaction speed is fast, and the maintenance amount is small.
3 Industrial applications
At present, the in-line zirconia oxygen measuring instrument has been widely used in the determination of the oxygen content of flue gas in boilers and heating furnaces, and the zirconia used for this purpose mostly adopts a tubular structure. The tube can be open at both ends or can be opened at one end. The latter is the most popular in the market. The inner and outer walls of the ZrO2 tube are coated with a porous Pt electrode, and the inner and outer electrodes are respectively extended toward the tube end and the NiCr wire is taken out at the end for signal output. Thereby controlling the combustion system to achieve low-oxygen combustion, to achieve the purpose of reducing thermal energy loss and saving energy.
4 Installation of zirconia oxygen meter
Reasonable installation is the key to ensuring reliable operation of the zirconia oximeter. Many of the problems are caused by improper installation.
4.1 Sampling measurement points
The determination of measuring points should follow the following principles:
(1) The selected measuring point requirements can correctly reflect the required furnace gas to ensure the authenticity of the oxygen sensor output signal, and try to avoid the return air dead angle;
(2) The measuring point should not be too close to the burning point or the nozzle. The gas in these parts is in a violent reaction, which will cause the oxygen sensor detection value to fluctuate sharply. Do not get too close to the gas generating equipment such as the fan to avoid the vibration damage of the motor. sensor;
(3) in a position to avoid possible collision to avoid collision damage to the probe, to ensure the safety sensor.
4.2 Installation and connection method of zirconia oxygen meter
(1) The installation of zirconia oximeter can be horizontal or vertical, and vertical installation is an ideal installation method. Regardless of the method used, the direction of the probe sampling tube guide plate should be as close as possible to the direction of the airflow to be measured. The initial direction can be determined by understanding the process during initial installation. To determine the better guiding direction, it is necessary to rotate the sampling tube direction after the system is energized and heated, and use a digital multimeter to observe the fluctuation of the output oxygen potential to determine.
(2) The joint used in the installation of the zirconia oxygen meter is a special flange joint. Asbestos pad crimping is required on the special joint to ensure sealing, otherwise the air leakage at the flange joint will affect the measurement accuracy or cause signal fluctuation.
(3) The signal lead-out line of the zirconia oxygen meter is preferably shielded to eliminate interference. The best way is to use two 2-core cables, one 2-core shielded cable to connect the oxygen potential output signal, and one 2-core kVV control cable to the probe heating connection. If the site conditions are not available, use a 4-core kVV cable to connect the probe oxygen potential signal to the heating terminal.
(4) a zirconium oxide oxygen analyzer calibration gas port is closed when the general testing, except that in the calibration gas; purge port connected to an air pump or compressed air lines, air purge port with a general solenoid valve controlled valves, constant open cycle 1, the purge gas introduced into the sampling line, the valve closes when the probe is detected, there can be other gases entering the sampling line. Compressed air was purged using compressed air must ensure that the probe does not contain water, i.e. the compressed air used must be gas-liquid separation process.
5 zirconia oxygen meter use and maintenance
5.1 connection heating control
The sampling and detecting probe can only work normally after the zirconia oximeter is connected with the heating control, and the random signal is a random signal, which does not mean any meaning. The zirconia oximeter can start normal gas detection at room temperature after receiving heating control. Generally, the zero adjustment of the probe is at room temperature. After heating the probe, the measurement of the air is performed. The digital output meter is used to measure the millivolt value of the probe output. This value is the zero deviation value of the probe. The zero is required to be added to the display instrument. The bit deviation is used to correct the oxygen concentration displayed by the meter.
5.2 Precautions when installing or replacing zirconia oximeter
When the zirconia oximeter is newly installed or replaced, the oxygen concentration display value of the oxygen analyzer should be corrected. Without this work, after replacing a new sensor, the detected oxygen concentration may deviate from the actual concentration, thus affecting the measurement accuracy.
5.3 Correction principle and method of oxygen concentration
The oxygen sensor directly measures the output of the measured gas and the standard air differential potential, called the oxygen potential. When the potential value is at zero (ie, air measurement), there is a deviation in the initial output potential of the different probes, and there may be an error in the output potential after the model converts the output oxygen concentration. Therefore, it is necessary to calibrate the probe signal in the oxygen analyzer. Otherwise, there will be a large deviation between the oxygen concentration and the oxygen concentration of the actual measured gas, which cannot meet the needs of on-site production, and even mislead control affects production.
The specific correction is generally calibrated by standard gas. The method is to pass the standard gas confirmed by the measurement and verification into the probe through the standard gas port. The output oxygen potential and the meter display oxygen concentration are measured. The meter shows that the oxygen concentration should be the same as the standard gas concentration. The deviation corrects the instrument linear parameters. The standard metering requirement uses at least 3 different standard gas calibration systems, so that the linear parameters of the system are corrected repeatedly after 3 calibrations to ensure the normal operation of the system.
5.4 Effect of dust accumulation on zirconia oxygen measuring instrument and purging and removing method Since zirconia oximeter is a long-term online measuring and measuring device, dust generated by boilers and other equipment (especially coal burning furnace or powder kiln) Blocking the gas sampling pipeline, causing the measured value to be distorted or even impossible to measure. At this time, the dust in the sampling tube must be purged regularly, and the length of the purge time is determined by the degree of dust accumulation. This purging method requires the zirconia oxygen measuring instrument to have the corresponding function or the supporting maintenance device. If there is no such device, only the manual valve can be installed to control the compressed air or the air pump periodically passes the purging port to perform dust removal work, but at this time The following must be noted:
(1) Since the oxygen potential of the oxygen sensor will decrease during the purging process, the lowest potential may drop to 1 to 2 mV. At this time, the detected oxygen potential does not represent the atmosphere in the furnace, and this must be noted;
(2) The flow rate of the purge air should be able to remove the ash accumulation. The oxygen potential output value should be paid attention to during the purge. If the oxygen potential value has not decreased, the air flow rate is too small, and the dust is not cleaned. It should be adjusted or checked. Purging the pipeline, the purge pipeline may have been blocked;
(3) The passage of the purge port is directly connected to the furnace. Each time after the purge is completed, the valve should be closed to block the purge hole to prevent the negative pressure air from entering the furnace and affect the detection of the oxygen sensor. When analyzing the quality of an oxygen sensor, it should be considered as a separate detection component. When detecting the oxygen potential of the oxygen sensor, all the wires connected to it should be disconnected, and the oxygen potential should be directly detected at the output of the oxygen sensor with a digital table with high internal resistance. By measuring the oxygen potential, it is compared with the value at normal use.
6 actual operation
Since 2003, China Petroleum Daqing Petrochemical Company's Chemical Plant No. 1 cracking furnace has adopted ZGP2+ZDT high-temperature in-line zirconia oxygen measuring instrument, which is mainly used for measuring the oxygen content of flue gas, participating in the combustion control of the cracking furnace, and operating stably. reliable. In May 2005, it was found that the deviation of the indication values ​​was large, and all of them were positive deviations, and it was judged that the gas path leaked. A zero point gas was passed through the standard gas line and the rotor flow meter was found to leak. Due to the negative pressure in the system under the measurement state, the outside air enters the person. Because the volume fraction of oxygen in the air is high, the measured value is high and normal after treatment. Some points to note in practice:
(1) The zirconia tube is required to work normally at 750cC, so the meter should be kept at a constant temperature;
(2) The gas pipeline must not leak;
(3) maintaining the injector in a stabilized air pressure of 0.15 MPa;
(4) Switch off the calibration standard gas injector air, open measurement;
(5) The presence of flammable gases such as H2, CO, and CH4 in the measurement gas will result in low measurement results.
references:
[1] Zhang Yi, Zhang Baofen, Cao Li, et al. Automatic detection technology and instrument control system [M]. Beijing: Chemical Press, 2005: 121-122.
[2] Wang Yonghong. Process detection instrument [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000:216-221.
[3] Wang Junjie. Detection Technology and Instrumentation [M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology Press, 2002: 241-423. (end)

Concerned about surprises
Tag: Zirconia Oxygen meter Oxygen concentration Platinum electrode Heating control
Previous: Effective separation of gas-liquid mixture Next: Using RADIOSS software to strengthen the roof of a certain model
Led Wall Mixer,Led Basin Faucet,Led Basin Mixer
Automatic Faucet Shower Series Co., Ltd. , http://www.sinyo-faucet.com